Parameter dependency
Use parameter dependency to dynamically limit the set of values available for one parameter by the value selected in another parameter. The functionality is based on object type relations existing in USU Service Management.
The parameter dependency section - examples below:
No dependencies exist for the edited parameter
The edited parameter is depending on another parameter
Another parameter is depending on the edited parameter.
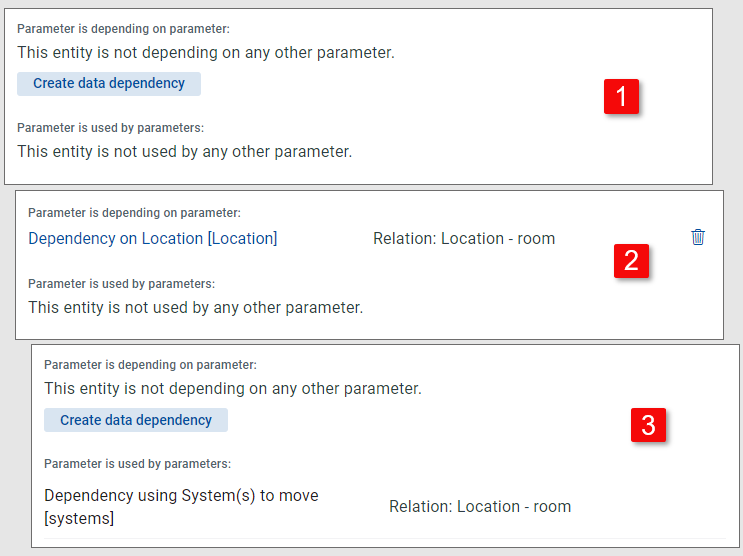
Parameter is depending on parameter: | Section covering the edited parameter's dependency on another parameter. If no dependency exist, use the Create data dependency button to create one. Click an existing dependency to open it for editing, Click the trash can icon to delete the dependency. Note that only one dependency can be defined for a parameter. E.g. it is not possible to make the System parameter dependent on both Location and Organization unit. More complex dependencies can, however, be achieved by daisy-chaining single dependencies between different parameters (e.g. making Location dependent on Organization unit and System on Location). |
Parameter is used by parameters: | Section informing about another parameter's dependency on the edited parameter. Any changes to this dependency must be done from the other parameter's side. |
Example:
Let's consider an offer Move system to another organization unit containing, among others, business object parameters Location [currentLocation] and System(s) to move. Let's use parameter dependency to limit the set of systems offered for selection in the System(s) to move parameter only to systems related to the location previously selected in the Location [currentLocation] parameter. This means making the System(s) to move parameter dependent on the Location [currentLocation] parameter. Proceed as follows:
Open the System(s) to move configuration element for editing and click the Create data dependency button . Dialog Create data dependency opens.
In the Create data dependency dialog, go to the Available entity parameters dropdown. The dropdown lists all other entity (BO) parameters used in the offer. Select the Location [currentLocation] parameter.
At this point the application checks which relations between the two selected business object types exist and offers these relations for selection in the Relation dropdown. Select a relation which fits your filtering purpose, in this example standard USM relation Location - room registering the current location of the system.
Click the Create dependency button. The Create data dependency dialog closes.
Back in the configuration element editor of the System parameter, the Parameter is depending on parameter: field now displays Dependency on location [currentLocation] / Relation: Location - room.
Note: Conversely, on the Location [currentLocation] parameter the dependency will be listed in section Parameter is used by parameters.
Click the Update configuration element button. The Edit configuration element dialog closes and the newly created relation between Location and System is also registered in the Configuration elements section of Offer detail.
Clicking the Dependencies and rules link next to the System configuration element calls a popup window providing more information on the dependency.
Note that as the System parameter is now depending on the Location parameter, the Location parameter cannot be deleted unless the relation is removed.
When dependency cannot be created
A dependency cannot be created if:
there are no other entity parameters used in the offer. (Clicking the Create data dependency button then presents an information popup.)
no relation exists (on the USM side) between the parameters. (Information text There are no relations for the selected entity gets displayed upon source entity selection.)
End user perspective
Anytime the shop user changes the selection of object(s) in the source parameter, the following happens in the depending parameter:
The filtering condition for objects in the value list in the depending parameter is updated based on the dependency and the parameter value list changes accordingly.
If there is already a selection of objects in the depending parameter, each of the objects is checked to fit the new filtering condition / value list. If a selected object is part of the updated value list, it stays selected. If it is not included in the updated value list, the object is removed from the selection.
Removing object selection in the source parameter resets the value list in the depending parameter but the previously selected values remain selected. Selecting another object(s) in the source parameter triggers the above described check and updates the depending values selection.
If multi-selection is possible and used for the source parameter, then removing already selected objects from the source parameter also clears corresponding selected objects in the depending parameter until only one object remains in the source parameter. When the last source object is removed, the depending selection remains until another source object is selected, at which point the above described check triggers and the remaining depending values selection is updated.